| ||||
What Is Organic Chemistry?
Organic Molecules: Carbs, Proteins, Lipids & Nucleic Acids
Organic molecules are the chemicals of life, compounds composed of more than one type of element, that are found in, and produced by, living organisms.
The feature that distinguishes an organic from inorganic molecule
Article Summary: What substances are within the realm of organic chemistry? This article covers the main categories of naturally occurring organic macromolecules: carbohydrates, proteins, nucleic acids and lipids.
Carbohydrates, Proteins, Lipids & Nucleic Acids
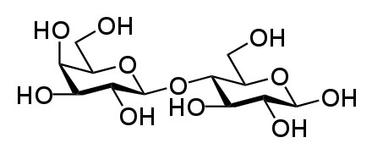
Lactose, a
disaccharide made of glucose and galactose.
 | ||||||
SPO VIRTUAL CLASSROOMS
is that organic molecules contain carbon-hydrogen bonds, whereas inorganic molecules do not. The four major classes of organic molecules include carbohydrates, proteins,
Carbohydrates
The term carbohydrate is actually a descriptor of what these molecules are composed of; carbon hydrates, in a ratio of one carbon molecule to one water molecule (CH2O)n. The word saccharide is a handy synonym for carbohydrate, because it can be preceded with a prefix indicating the size of the molecule (mono-, di-, poly-):
- Monosaccharides: The simplest, single sugars. Examples: Glucose and fructose are monosaccharides.
- Disaccharides: Double sugars that are a combination of two monosaccharides. Example: Sucrose (table sugar) is made of glucose and fructose together.
The Virtual Cell Biology Classroom provides a wide range of free educational resources including Power Point Lectures, Study Guides, Review Questions and Practice Test Questions.
Page last updated: 10/2016
FREE Printable
study aid.
See Organic Chemistry Lecture PPT for info that will help you complete this table.
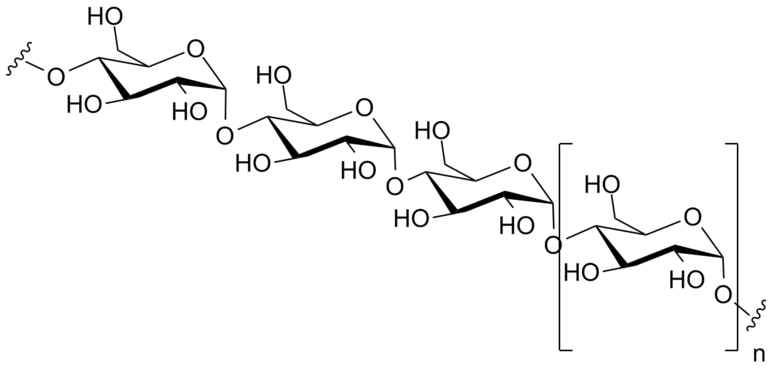
- Polysaccharides: These are polymers composed of several sugars. They can be one type of monomer (many of same monosaccharide) or mixture of monomers. Example: Starch is a polysaccharide composed of many glucose molecules.
Amylose, a linear polymer of glucose can be made of thousands of glucose units. Amylose and amylopectin are the two components of starch.