| ||||
Types of Growth Media to Culture Bacteria - P3
SPO VIRTUAL CLASSROOMS
SPO VIDEO:
Mannitol Salt Agar
(MSA) Microbiology Lab Tutorial
PAGE 3 < Back to Page 2
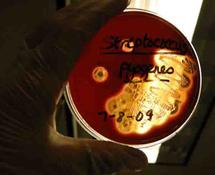
Another specialized medium, Blood Agar (BAP) contains sheep’s blood. If bacteria growing on the medium produce exotoxins that hemolyze (cut up) the red blood cells, the medium changes color.
BAP medium that has changed from red to transparent (completely clear) indicates beta-hemolysis, and possibly the strep throat pathogen Staphylococcus pyogenes. BAP that is bruised (alpha-hemolysis) or unaffected by bacterial growth present (gamma hemolysis) indicate normal flora, non-pathogenic bacteria.
More Materials on Specialized Bacterial Growth Media
- Identifying Bacteria Laboratory Exercise Main Page.
- Microbiology Video Library from Science Prof Online.
- Bacterial Growth Media Images from SPO.
SPO VIDEO:
Blood Agar
(BAP) Microbiology Lab Tutorial
Blood Agar, a nutrient-rich medium containing sheep's blood. Beta-hemolytic bacteria, such as pathogen
Streptococcus pyogenes change this medium from solid red to clear.
Bacteria that grow on
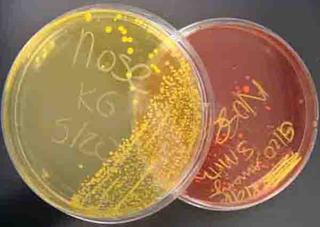
Mannitol Salt Agar (MSA) are all salt-loving halophiles. Salt is what makes this medium selective.
MSA also contains the sugar-alcohol mannitol (food) and a pH sensitive dye. This is the differential aspect of the medium.
If bacteria that cannot eat mannitol are growing on MSA (such as the normal flora species Staphylococcus
epidermidis) the medium remains pink. If halophilic bacteria that are able to eat mannitol are growing, (such as the pathogen Staphylococcus aureus), the pH sensitive dye is triggered by bacterial waste and the medium changes to bright yellow.
FREE Printable
Study Aid, from Tami. You'll brain will thank me!
SCIENCE VIDEOS
Page last updated: 8/2016