| ||||
Blood Agar Bacterial Growth Medium
Differential Medium to Identify B-hemolytic Streptococcus
A growth medium (plural: media) is a mixture of nutrients, moisture and other chemicals that bacteria require for growth. Media are used to grow bacterial colonies (millions of bacteria having arisen through the binary fission of a single progenitor).
Article Summary: Blood Agar is a bacterial growth medium that can distinguish normal from pathogenic bacteria based on the effect of bacterial hemolytic exotoxins on red blood cells.
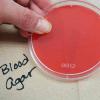
Blood Agar (BAP) Bacterial Growth Medium
SCIENCE PHOTOS
SPO VIRTUAL CLASSROOMS
 | ||||||
SCIENCE VIDEOS
Using Media to Identify Bacteria
Some media can be used to do more than just grow bacteria; specialized agars can aid in bacterial identification.
Blood Agar Is Not a Selective Medium
If a bacterial growth medium is selective, that means that it grows only certain types of microbes while inhibiting the growth of other types of microbes. Blood agar is an enriched medium that provides an extra rich nutrient environment for microbes. Therefore, BAP is not a selective growth medium, since it supports the growth of a wide range of organisms.
Blood Agar Is a Differential Medium
A growth medium is considered differential if, when specific microbes are present, the medium or bacterial colonies themselves exhibit a color change that provides information about their identity.
Page last update: 4/2016
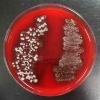
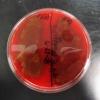
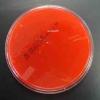
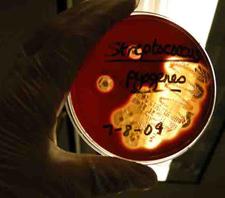
PHOTOS OF BLOOD AGAR: 1. Sterile plate of Blood Agar (BAP); 2. Bacterial growth from two throat cultures plated on Blood Agar. To see hemolysis patterns, it is best to look at the bottom of the plate, not the top; 3. Beta hemolysis on Blood Agar indicating presence of pathogen Streptococcus pyogenes. (Note red color has disappeared around the bacterial growth and those areas of the media are transparent.) 4. Alpha hemolysis on BAP indicating the growth of normal flora; 5. Gamma hemolysis is when the growth on BAP does not affect the appearance of the agar. This also indicates normal flora.
Click here for more photos.
Blood agar (BAP) is a differential growth medium which microbiologists use to distinguish clinically significant bacteria from throat and sputum cultures. BAP contains 5% sheep blood. Certain bacteria produce exotoxins called hemolysins, which act on the red blood cells to lyse, or break them down.
Blood agar growing pathogen, Beta-hemolytic Streptococcus progenies..
See Page 2 for a VIDEO on how to interpret Blood Agar (BAP)!
You have free access to a large collection of materials used in two college-level introductory microbiology courses (8-week & 16-week). The Virtual Microbiology Classroom provides a wide range of free educational resources including PowerPoint Lectures, Study Guides, Review Questions and Practice Test Questions.