| ||||
What Is the pH Scale?
Measurement of Acidity & Alkalinity
What Is an Acid?
An acid is any ionic compound that releases hydrogen ions (H+) in solution. Ionic compounds are molecules held together by ionic chemical bonds that result from the attraction of oppositely charged atoms, called ions.
Article Summary: The pH scale is a measurement of the acidity or alkalinity of a solution. To understand the scale, it is important to first understand what acids and bases are.
Acids, Bases, Buffers, and the pH Scale
 | ||||||
Need Help with Chemistry?
SPO offers free PowerPoint lectures, sample test
questions, review questions and assignments on many different science topics.
Below are links to those that relate to chemistry:
 | ||||||
SPO VIRTUAL CLASSROOMS
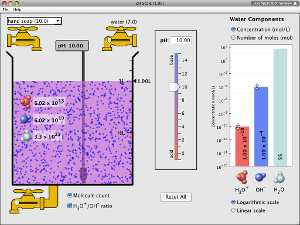
Interactive pH Scale Simulation
UNIVERSITY OF COLORADO
Test the pH of things like coffee, spit, and soap to determine whether each is acidic, basic, or neutral. Visualize the relative number of hydroxide ions and hydronium ions in solution. Switch between logarithmic and linear scales.
Must have updated version of Java to run simulation.
Weak acids release fewer hydrogen ions and have a sour taste. Strong acids release more hydrogen ions and are highly corrosive. The more hydrogen ions in the solution, the more acidic it is.
What Is a Base?
Bases, also called alkaline substances, are compounds that release hydroxyl ions (OH-) in solution. Weak bases have a bitter taste (opposed to sour taste of acids and sweetness of aldehydes and ketones) and are slimy to the touch. The more hydroxyl ions in a solution, the more alkaline it is.
You have free access to a large collection of materials used in a college-level introductory Cell Biology Course. The Virtual Cell Biology Classroom provides a wide range of free educational resources including Power Point Lectures, Study Guides, Review Questions and Practice Test Questions.
Page last updated: 8/2015
Measurements
of pH
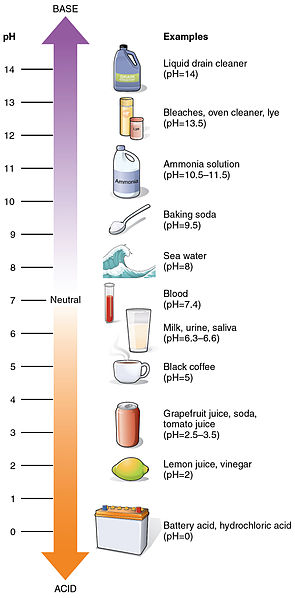
Acidity or alkalinity of a solution is measured by concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) versus hydroxyl ions (OH-) and is expressed as pH level, an exponential scale that ranges from 0 (very acidic) to 14 (very basic).
Because the scale is logarithmic, a change of just one unit represents a tenfold change in H+ concentration. When the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) equals the concentration of hydroxyl ions (OH-) a solution is neutral.