| ||||
Nucleic Acid Function
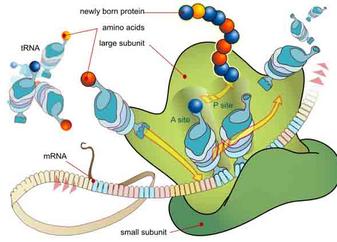
DNA Replication, Transcription & Translation
When the DNA molecule is inactive, the bases are linked by these hydrogen bonds and the molecule is in its spiral-shaped state. When DNA is being used—either being copied (a process called replication) or being employed to build proteins (involving the processes of transcription and translation)—the DNA molecule must be opened up, essentially “unzipped” between the bases.
Article Summary: Nucleic acids, DNA and RNA, are the vital genetic blueprints for and builders of cellular proteins. Here is how DNA is copied and proteins are built.
Nucleic Acid Function: Replication & Gene Expression
Page last updated: 8/2015
 | ||||||
SPO VIRTUAL CLASSROOMS
Nucleic Acid Structure
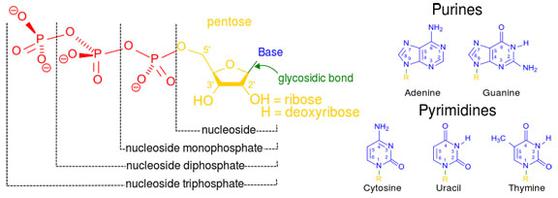
Nucleic acids are large organic molecules made of building blocks called nucleotides. Each nucleotide has three main parts:
- a pentose sugar called ribose
- one or more phosphate groups
- one of five cyclic nitrogenous bases
Phosphate-Sugar Backbone
Nucleotides are linked to each other by covalent bonds between phosphate of one nucleotide and sugar of next. Linked nucleotides are the phosphate-sugar backbone of nucleic acids, and their nitrogenous bases extend from this phosphate-sugar backbone like teeth of a comb.
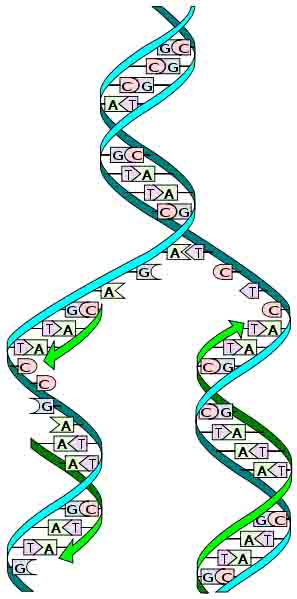
The DNA Spiral Staircase
In deoxyribonucleic acid, DNA, hydrogen bonds form between specific bases of two nucleic acid chains, forming a twisted, double-stranded DNA molecule that looks like a spiral staircase, with the two sugar-phosphate chains as side rails and the base pairs forming the rungs.
DNA only contains the bases Adenine (A), Cytosine (C), Guanine (G) and Thymine (T), not Uracil (U). When bases pair up between the two DNA strands, a purine always pairs with a pyrimidine. Specifically Adenine and Thymine always pair up, and Cytosine (C) and Guanine (G) always pair up.
The Virtual Cell Biology Classroom provides a wide range of free educational resources including Power Point Lectures, Study Guides, Review Questions and Practice Test Questions.
The bases found in nucleic acids include the double-ring purine bases Adenine and Guanine the single-ring, smaller pyrimidine bases of Cytosine, Uracil and Thymine.
of Science Prof Online
You have access to a large collection of free science teaching materials used in high school and college-level introductory science courses. The SPO Instructors Corner has resources for teaching general science, anatomy & physiology, chemistry, cell biology genetics, immunology and microbiology.