| ||||
Nucleic Acid Function: Replication - P2
SPO VIRTUAL CLASSROOMS
Page last updated: 8/2015
PAGE 2 < Back to Page 1
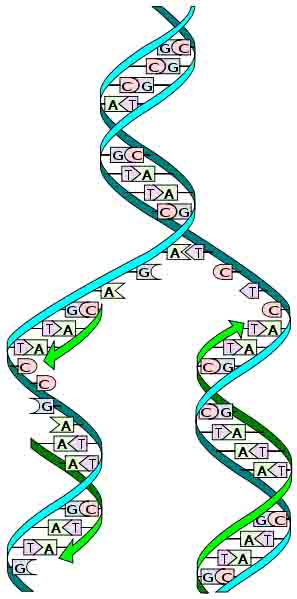
DNA Replication
The process of copying the double-stranded DNA molecule is called replication. Cells must replicate their DNA before dividing, so that each new cell has a complete copy of instructions.
Prokaryotes, like bacteria, replicate their DNA (the nucleoid) throughout the interval between cell divisions.
In eukaryotes, the timing of replication in the nucleus is highly regulated.
Semi-conservative Replication
Each double stranded DNA molecule holds the same genetic information.
Therefore each strand can serve as a template for the construction of a new strand. The template (original) strands are separated and preserved, while the new strands are assembled from nucleotides.
The Virtual Cell Biology Classroom provides a wide range of free educational resources including Power Point Lectures, Study Guides, Review Questions and Practice Test Questions.
This is called semi-conservative replication, since the each of the two resulting DNA molecules consist of one conserved old strand and one brand new strand. These resulting double-stranded DNA molecules, blended from old and new, are identical to each other.
VIDEO
DNA Structure & Replication
from
Crash Course Biology
See Page 3 for homework assignment and other free teaching materials on Molecular Genetics!