| ||||
Bacteria Growth Media & Cultures Photos
Science Image Library
Bacterial Growth Media & Cultures Laboratory
from Science Prof Online
 | ||||
You have free access to a large collection of materials used in a college-level introductory microbiology course. The Virtual Microbiology Classroom provides a wide range of free educational resources including PowerPoint Lectures, Study Guides, Review Questions and Practice Test Questions.
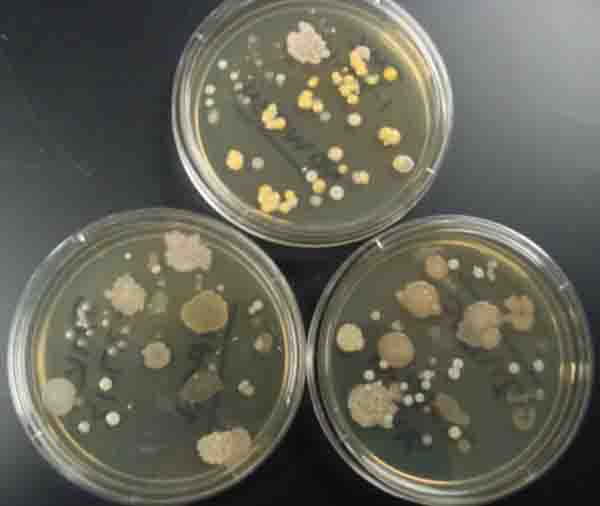
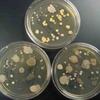
1. Arm plate applied to inside of forearm to collect a bacterial sample; 2 & 3. Arm plate after incubation. Note variety of bacterial colonies.
Arm Plate Photos (Click on photo to enlarge.)
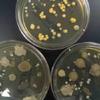
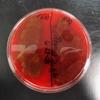
1 & 2. Touch plates: Top plate touched with dirty hands, bottom left plate touched with washed hands and bottom right plate touched with scrubbed + alcohol hands. 3. Another set of touch plates. Top plate was touched with dirty hands, bottom left plate with washed hands and bottom right plate with scrubbed + alcohol hands. For all photos, note that diversity of microbial growth decreases when hands are washed; 4. Close up of a touch plate showing a variety in colony morphology.
Touch Plate Photos (Click on photo to enlarge.)
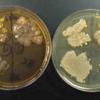
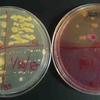
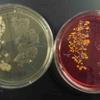
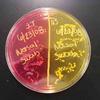
1 & 2. Top and bottom view of environmental samples (kitchen counter, kitchen sink, bathroom counter, bathroom sink) plated on MacConkey's agar (left) and TSY (right); 3. Kitchen sink environmental sample plated on TSY (bottom). MacConkey's (top) shows growth of pink lactose fermenters, 4. Bottom view of another set of environmental samples, TSY on left and MacConkey's on right.
Environmental Samples Photos (Click on photo to enlarge.)
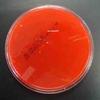
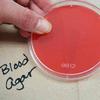
1. Sterile plate of Blood Agar; 2 & 3. Top and bottom view of Blood Agar plated with throat culture and showing alpha hemolysis cause by normal flora; 4. Plate of Blood Agar plated with Streptococcus pyogenes and showing beta hemolysis. 5. What a plate would look like, from bottom, of showing gamma hemolysis (no hemolysis).
Throat Swab on Blood Agar Photos (Click on photo to enlarge. See more.)
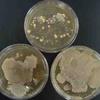
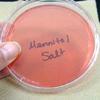
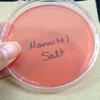
1. Sterile plate of Mannitol Salt Agar; 2. Top view of nasal culturel samples, TSY on left, MSA on right. Bacteria on MSA are normal flora; 3. Top view of two nasal cultures. Left shows growth of mannitol fermenter (agar turns yellow), right shows growth of nonmannitol fermenter (agar stays pink); 4. Bottom view of same plate; 5. Punctiform bacterial colonies of normal nasal flora Staphylococcus epidermidis.
Nasal Swab on TSY & Mannitol Salt Photos (Click on photo to enlarge. See more.)
Page last updated 5/2014
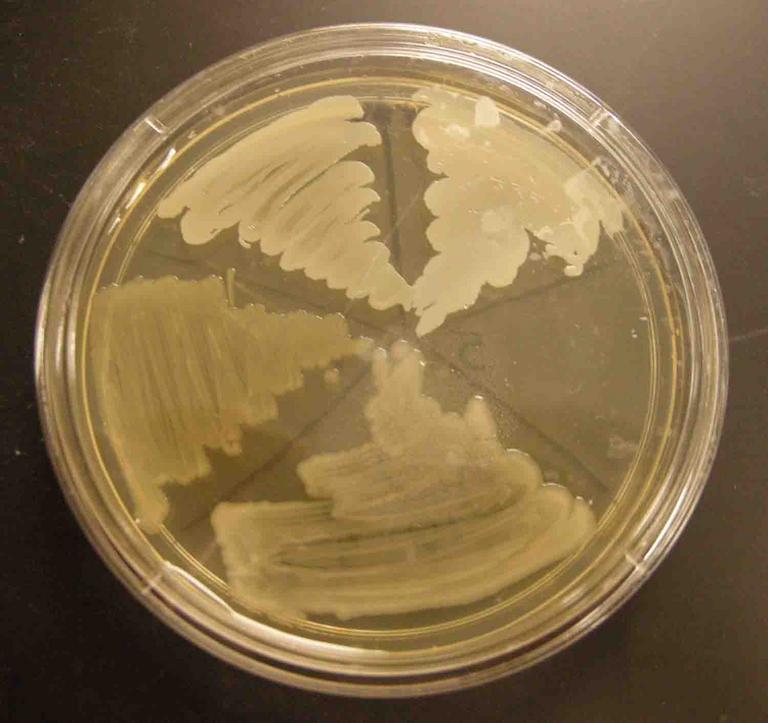
Need help remembering what the media plates looked like when they were sterile, before bacteria began to grow? 1. TSY being inoculated; 2. Blood agar (BAP); 3. Mannitol Salt (MSA); MacConkey's (MAC); 5. Clockwise from top left: MAC, MSA BAP (bottom).
Sterile Media Photos (Click on photo to enlarge.)
Didn't find what you need?
Search SPO for a Photo
VIDEO: Mannitol Salt Agar (MSA) Specialized
Bacterial Growth Medium
Go to > Article on Mannitol Salt Agar
SPO VIRTUAL CLASSROOMS
 | ||||||
 | ||||||
SPO is a FREE science education website. Donations are key in helping us provide this resource with fewer ads.
Please help!
(This donation link uses PayPal on a secure connection.)
SCIENCE VIDEOS
Science Prof Online has a continuously growing collection of free science images. The images on this page are related to the Virtual Microbiology Classroom Bacterial Growth Media & Cultures Laboratory Exercise.
If you use one of our images, we just ask that you give us credit and provide a link to the SPO website. To save an image below to your computer, right click on it and select "Save". Click on image to enlarge.
For those in need of high-resolution images, we will soon be offering hi-res files of many photos in the Science Image Library. Follow us on Twitter @ScienceProfSPO to get updates on new SPO features and products.
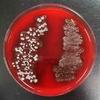
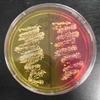
MacConkey's Agar (MAC) Photos (Click on image to enlarge. See more)
1.Sterile MacConkey's Agar; 2. MacConkey's Agar growing Gram-negative bacteria. Left plate growing lactose-negative Salmonella, right plate growing lactose-positive E. coli; 3. "Ecoli" written on MAC using Lac+ E. coli bacteria; 4. Pink, lac+ colony growing on MAC above a tan lac- colony; 5. Smiley face of lac+, Gram- bacteria growing on MAC.
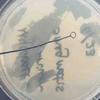
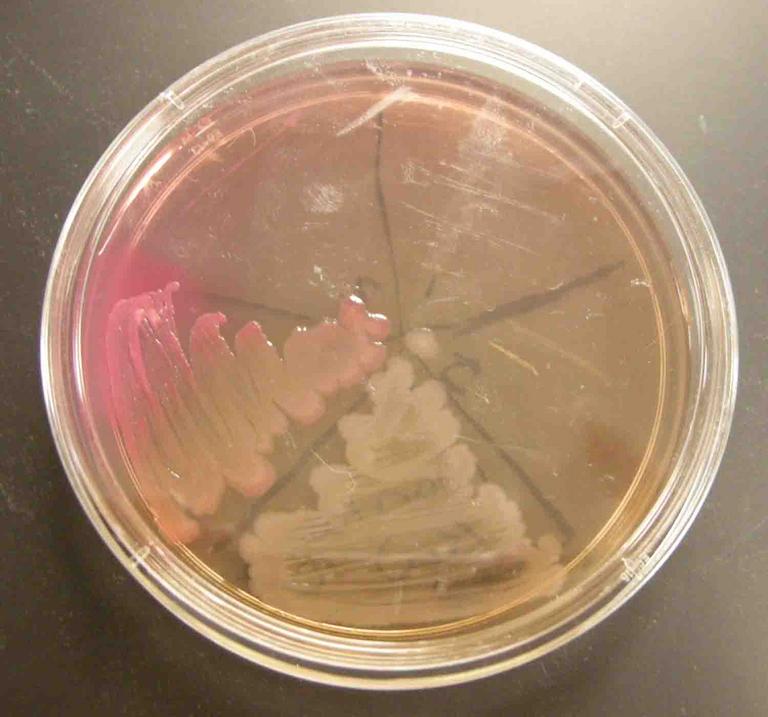
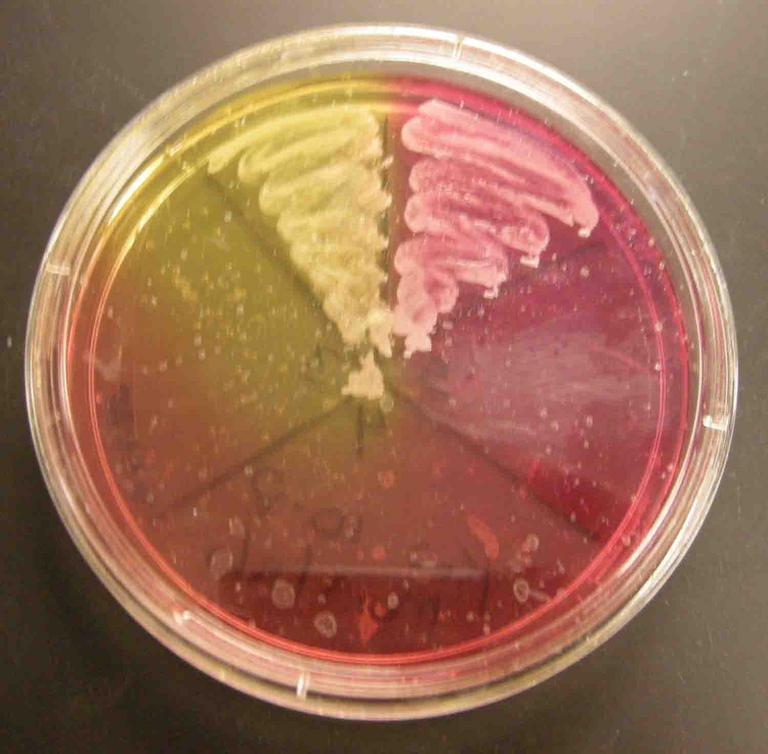
TSY, MacConkey's and Mannitol Salt Agars (left to right) inoculated with the following samples (clockwise from top left on each plate): Staph aureus, Staph epi, sterile loop, Salmonella, E. coli.
 | ||||
Our Favorite New Microbio APP!
Cool infectious disease game:
Plague Inc.
Do you have what it takes to be a successful pathogen?
VIDEO: How to Interpret MacConkey's Agar (MAC) Bacterial Growth Medium
Go to > Article on MacConkey's Agar
Bacterial Controls Photos (Click on photo to enlarge.)
More Bacterial Growth Media & Cultures Resources
- Comparison of Liquid & Solid Bacterial Growth Media "class notes"article from Science Prof Online.
- Aseptic Technique to Pour Bacterial Growth Media Into Petri Dishes "class notes"article.
- Differential & Selective Bacterial Growth Media "class notes" article.
- Types of Culture Media for Growing Bacteria "class notes" article.