| ||||
Gram Negative Bacteria
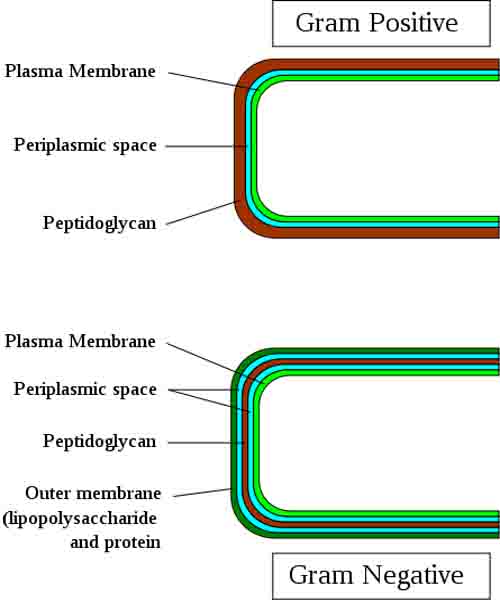
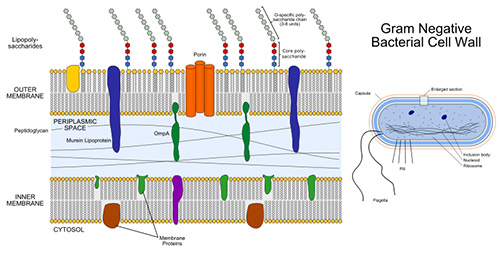
Gram- Bacterial Cell Wall Structure
Nearly all types of bacteria have a cell wall containing peptidoglycan, a chemical unique to bacteria. The rigid structure of the bacterial cell wall is due to securely linked peptidoglycan molecules that surround the plasma membrane, giving these prokaryotes
shape and protection.
Gram- Cell Wall
Peptidoglycan: From the peptidoglycan inwards bacterial cells are very similar. Going further out, the bacterial world divides into two
major groups:
Gram positive (G+)
& Gram negative (G-).
Article Summary: Most bacteria have one of two possible types of cell walls. Here are the features of the Gram- bacterial cell wall that distinguish it from Gram+.
Gram-negative Bacterial Cell Wall
SPO VIRTUAL CLASSROOMS
 | ||||||
The cell walls of Gram- bacteria are more chemically complex, thinner and less compact, with peptidoglycan comprising only 5 – 20% of the structure.
LPS Membrane: In gram-negative bacteria, peptidoglycan is not the outermost layer of the cell wall. Gram- cells have an additional, external membrane, similar to the plasma membrane, but less permeable and composed of lipopolysaccharides (LPS); a harmful substance classified as an endotoxin.
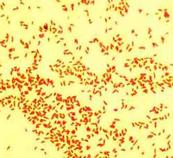
Gram-negative Escherichia coli @ 1000xTM
The Gram Stain
Once scientists understood that infectious disease was caused by microorganisms (Germ Theory), it was imperative to find a way to view bacteria and other microbes; because in addition to being microscopic, most bacteria colorless.
In the 1800’s, Christian Gram, a Danish bacteriologist, developed a technique for staining bacteria that is still widely used today. The Gram stain protocol involves the application of a series of dyes that leaves some bacteria purple (Gram+) and others pink (Gram-).
Page last updated: 11/2015
You have free access to a large collection of materials used in a college-level introductory microbiology course. The Virtual Microbiology Classroom provides a wide range of free educational resources including PowerPoint Lectures, Study Guides, Review Questions and Practice Test Questions.
H. C. Gram