| ||||
Bacterial Cell Wall Structure: Gram + & Gram - P2
You have free access to a large collection of materials used in two college-level introductory microbiology courses (8-week & 16-week). The Virtual Microbiology Classroom provides a wide range of free educational resources including PowerPoint Lectures, Study Guides, Review Questions and Practice Test Questions.
Gram-negative Cells
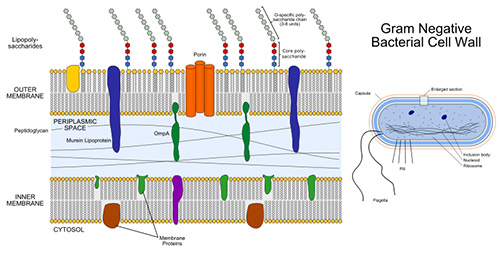
The cell walls of Gram-negative bacteria are more chemically complex, thinner and less compact.
Peptidoglycan makes up only 5 – 20% of the cell wall, and is not the outermost layer. The peptidoglycan of Gram-negative bacteria is located between the plasma membrane and an outer, LPS membrane.
This LPS membrane is similar to the plasma membrane, but is less permeable and is composed of lipopolysaccharides (LPS). LPS is a harmful substance classified as an endotoxin.
Page last updated 3/2016
SPO VIRTUAL CLASSROOMS
SCIENCE VIDEOS
Peptidoglycan and Antibiotics
Penicillins and cephalosporin antibiotics interfere with the linking of the interpeptides of peptidoglycan, but because of the LPS membrane, these antimicrobials can’t access the peptidoglycan of gram-negative bacteria. Gram-positive bacteria, with no membrane outside the peptidoclycan cell wall, are more susceptible to these antibiotics.
Cell walls without intact peptidoglycan cross-links are structurally weak, and disintegrate when cells divide. This is how penicillins and cephalosporins work to disable bacteria.
Since the eukaryotic cells of humans do not have peptidoglycan cell walls, our cells are not damaged by antibiotics that target peptidoglycan, and microorganisms that do not contain peptidoglycan are also not susceptible to these drugs.
SPO VIDEO: How to Do a
Gram Stain
Gram-negative Escherichia coli @ 1000xTM. Go to >
PAGE 2 < Back to Page 1
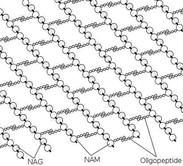
Bonding structure of peptidoglycan in bacterial cell wall, with strings of sugars (NAG and NAM) held together with peptide bridges.
Sources
- Bauman, R. (2014) Microbiology with Diseases by Taxonomy 4th ed., Pearson Benjamin Cummings.
The space between the cell wall and the plasma membrane is called the periplasm. Periplasm controls molecular traffic entering and leaving the cell.