| ||||
Aseptic Technique to Reduce Contamination - P2
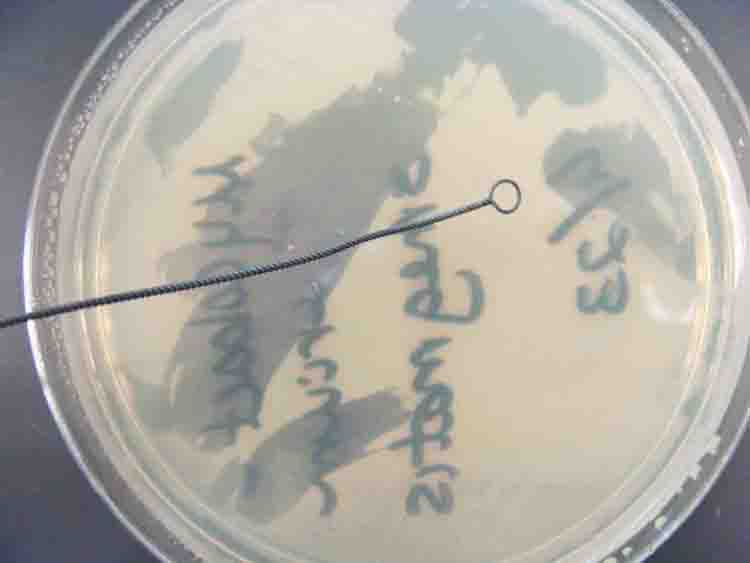
Plate of TSY agar being inoculated using the loop.
SPO VIRTUAL CLASSROOMS
SCIENCE VIDEOS
Page last updated:
8/2015
You have free access to a large collection of materials used in a college-level introductory microbiology course. The Virtual Microbiology Classroom provides a wide range of free educational resources including PowerPoint Lectures, Study Guides, Review Questions and Practice Test Questions.
The SPO website is best viewed in Microsoft Explorer, Google Chrome or Apple Safari.
Asetpic Technique for Transferring Bacteria
Once a growing medium is poured into a Petri dish and cooled, it is referred to a “plate.” Plates are made ultimately to be inoculated, that is, have a tiny amount of a pure bacterial culture or a clinical sample streaked across the surface. After inoculation, the plate is usually incubated for at least 24 hours to encourage growth of the sample.
Sterilize Inoculation Loop: Bacterial inoculate can be transferred using an inoculation loop (a.k.a. inoculation wand).
PAGE 2 < Back to Page 1
This instrument is essentially a wire with a small loop at one end and a handle at the other. Since it is made of metal, it can be repeatedly used and then resterilized in a flame or microincinerator.
Allow Loop to Cool: After sterilizing the loop, it must cool briefly, so as not to kill organisms in the sample being transferred. When waiting for the loop to cool, do not wave it around to hasten cooling, and certainly don’t blow on it. Either action could introduce bacterial contamination.
Transfer Bacteria: Once the wand is sterilized and cooled, the bacterial inoculate can be obtained from the source plate and then transferred to the new plate. Streak plate technique is typically used to introduce a pure bacterial sample to a new plate and spread that sample out sparsely enough to facilitate the growth of distinct bacterial colonies.
Microincinerator used to sterilize inoculation loops.
Sources and Resources
- Schauer Cynthia (2007) Lab Manual to Microbiology for the Health Sciences, Kalamazoo Valley Community College.
- Bauman, R. (2014) Microbiology with Diseases by Taxonomy 4th ed., Pearson Benjamin Cummings.
- Bacterial Growth Media & Cultures Laboratory Exercise Main Page from the Virtual Microbiology Classroom.
- Aseptic Technique and the Transfer of Microorganisms, Virtual Amrita Laboratories
- Microbiology Lab Flashcards from Quizlet
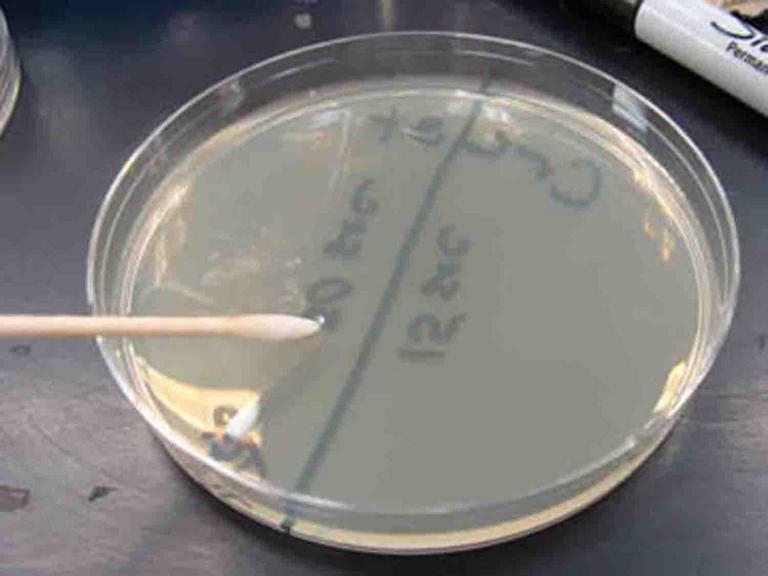
When clinical samples are plated, a sterile swab is used to obtain the biological sample from the patient (such as throat swab) and to transfer that sample to a plate.