| ||||
Genetics Terminology:
Chromosomes & Sister Chromatids
CLASS NOTES from Science Prof Online
Nuclear and Cellular Division
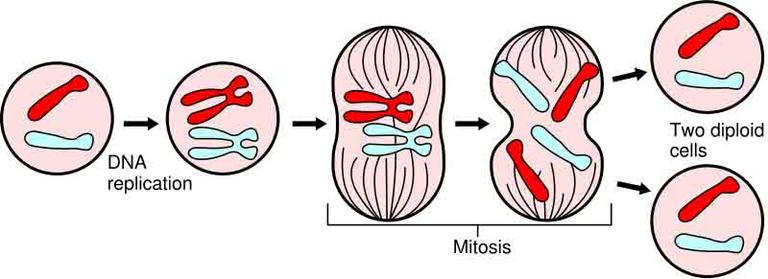
During nuclear division, the chromosomes line up at the cell's equator and then the sister chromatids separate and move to opposite ends of the cell (poles). Once separated these former sister chromatids are now each considered a chromosome.
Article Summary: When is DNA considered a chromosome? What is a sister chromatid and how does it differ from a chromosome? This article unravels some of the lingo of DNA.
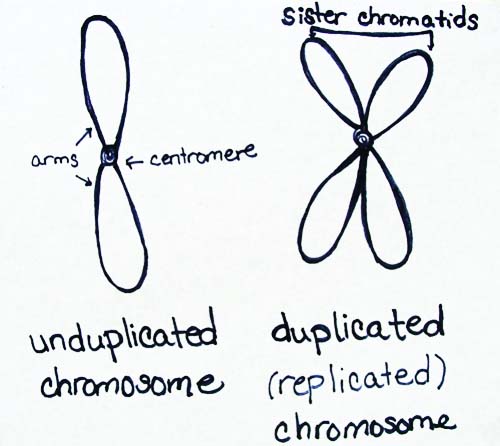
Duplicated Chromosomes vs. Sister Chromatids
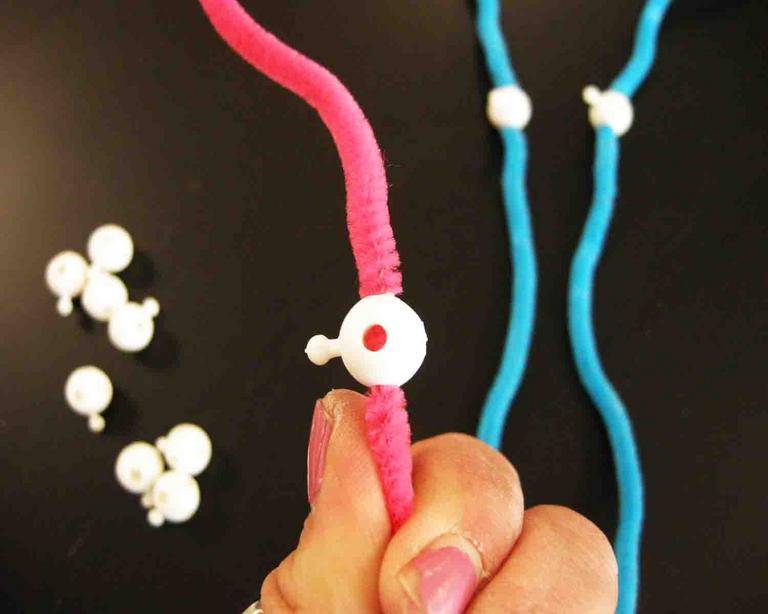
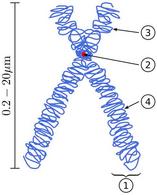
Two joined sister chromatids:
1) Chromatid, (2) Centromere,
(3) Short arm, (4) Long arm
Preparing for Nuclear Division
For most of the cell cycle, the DNA molecules are in very long strands called chromatin. But when the cell prepares to divide, it must pack its DNA for the move. So prior to cell division, the chromatin condenses. This replicated DNA molecule, in its condensed form, is now referred to as a chromosome.
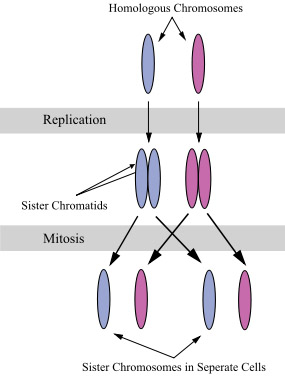
Students often become confused when it comes to the genetics terminology associated with chromosomes and chromosome number. What are homologous chromosomes? What are duplicated chromosomes?
Sources & Resources
- Genetics: Tour of the Basics, Genetic Science Learning Center, University of Utah.
- Genetics Terminology: Duplicated vs. Homologous Chromosomes.
- Chromosome Structure animation from John Kyrk.
- How the Cell Cycle Works, animation & quiz from McGraw-Hill.
- Mitosis & Cytokinesis, animation & quiz from McGraw-Hill.
- Comparison of Mitosis & Meiosis animation & quiz from McGraw-Hill.
- Cell Division: Mitosis Lecture Main Page, Virtual Cell Biology Classroom.
- Cell Division: Meiosis Lecture Main Page, Virtual Cell Biology Classroom.
In the illustration above, the third cell shows 4 sets of sister chromatids (joined, duplicated chromosomes) lined up at the cell's equator. In the fourth cell, these sister chromatids have separated from each other into 8 daughter chromosomes.
 | ||||||
SPO VIRTUAL CLASSROOMS
Copying DNA
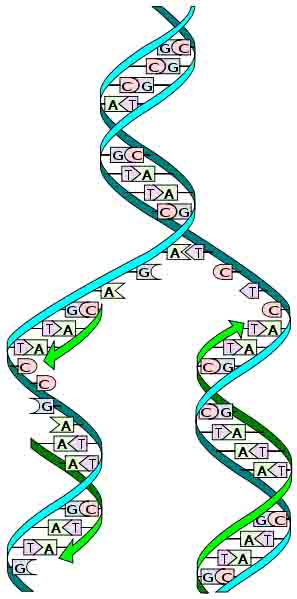
Before a cell divides, it must make a copy of its DNA (nucleic acid) so that each daughter cell has a complete copy of genetic information. Each individual DNA molecule is the material of one chromosome, and the process of copying the DNA is called replication.
Semi-conservative Replication
DNA is a double-stranded molecule. Each strand holds the same genetic information. Therefore each strand can serve as a template for the production of a new strand. The template strand is preserved and the new strand is assembled from nucleotides (the small monomers that together make nucleic acids). The resulting double-stranded DNA molecules are identical, and are linked together until the process of nuclear division (separation of the duplicated genetic material).
You have free access to a large collection of materials used in a college-level introductory Cell Biology Course. The Virtual Cell Biology Classroom provides a wide range of free educational resources including Power Point Lectures, Study Guides, Review Questions and Practice Test Questions.
Page last updated: 10/2015
The SPO website is best viewed in Microsoft Explorer, Google Chrome or Apple Safari.
 | ||||||
SPO is a FREE science education website. Donations are key in helping us provide this resource with fewer ads.
Please help!
(This donation link uses PayPal on a secure connection.)
You have FREE access to a large collection of materials used in a college-level introductory biology course. The Virtual Biology Classroom provides a wide range of free educational resources including PowerPoint Lectures, Study Guides, Review Questions & Practice Test Questions.
 | ||||
WHICH GENETIC TRAITS DO YOU HAVE?
What are chromatids? How do all of these terms differ and how do they relate to each other? To understand these terms, we must first review cell division.
Cells Divide to Make More Cells
During the cell cycle, somatic cells (non reproductive cells) of eukaryotic organisms grow and divide. In this process, called mitosis, a single cell ('parent cell') splits into two identical 'daughter cells'.
DNA molecule replicating: Strands separating so that the DNA can be read and replication can occur.
But, remember, there are two copies attached to each other until nuclear division. Each of the two copies of a chromosome are designated as a sister chromatid and they are physically linked together at a point on the chromosome called the centromere.
Once the chromosomes move to opposite poles, the dividing cell reforms a nuclear membrane around each of the two areas of separated genetic material. The cell itself then proceeds to divide in a process called cytokinesis, and what was once one cell becomes two, completing the process of mitosis.