| ||||
Eukaryotic Cell Structures, Functions & Diagrams - P3
SPO VIRTUAL CLASSROOMS
Sources and Helpful Eukaryotic Cell Links
- Becker, W. M. et. al. (2009) The World of the Cell. Pearson Benjamin Cummings.
- Eukaryotic Cell Interactive Animation from Cells Alive.
- Inside a Cell, interactive cell diagram from University of Utah.
- Eukaryotic Cell Animation interactive exercise from Sumanas.
- Golgi Apparatus animated tutorial.
- Vesicle Budding & Fusing from Sumanas.
- Cell Structure Interactive Animation from Wiley.com.
PAGE 3 < Back to Page 2
- Microtubule Organizing Center (MTOC): This structure is where microtubules are assembled and anchored. In animal cells the MTOC is called the centrosome, which consists of two centrioles. In plant cells, the nuclear envelope appears to function as the main MTOC.
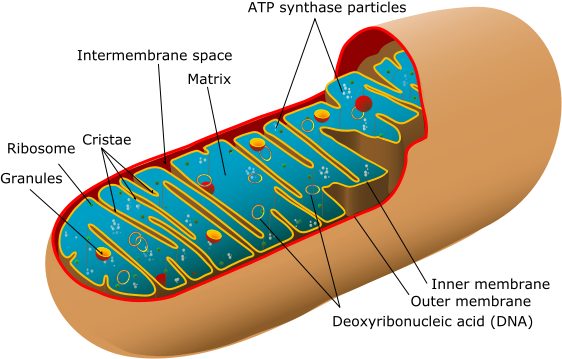
- Mitochondria: These tiny powerhouses of the cell, are double-membrane bound organelles that extract energy from food to produce ATP (adesnosine-5’- triphosphate), a multi-purpose molecule that carries energy for use within the cell.
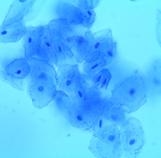
Human Cheek epithelial cells stained with methylene blue and viewed at 400xTM.
FREE Educational Materials on Cell Structure
Page last updated: 3/2016
End of article ...
Other Eukaryotic Cell Components and Organelles
- Cytoplasm: The inside of the cell, between the nucleus and plasma membrane, is filled with a gel-like fluid in which the organelles are suspended. Cytoplasm includes both the liquid (called cytosol) and the suspended organelles.
- Cytoskeleton: Composed of microtubules, intermediate filaments and microfilaments, this network of fibers provides an inner framework for the cell. The cytoskeleton supports the cells structure, anchors and helps transport organelles, and aids in cell division.
MITOCHONDRION
SPO VIDEO: How to Make a Wet Mount of Stained Epithelial Cheek Cells
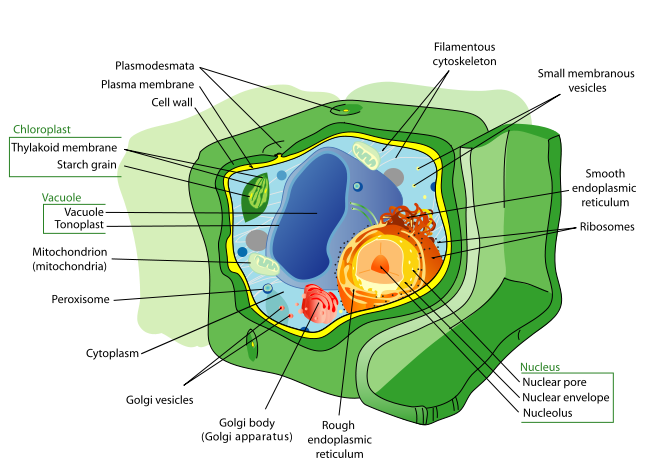
Structures Present in Plant Cells
Plants are eukaryotes that have some features not found in animal eukaryotic cells:
- Cell wall: Plant cells have protective cell walls, composed mainly of structural carbohydrates. The cell wall provides support, helps maintain cell shape, and prevents the cell from taking on too much water and bursting. The cell wall is not a feature unique to plants; bacteria, fungi and some protists also have cell walls.
- Central vacuole: The central vacuole takes up most of the space within a plant cell. Defined by a membrane called the tonoplast, the central vacuole functions as a holding tank for water and other molecules used by the cell. When full of water, the vacuole presses the other cell contents against the boundary of the cell.
- Chloroplasts: These double membrane bound organelles contain the green pigment chlorophyll, which captures sunlight energy, so that the cell can produce its own food, a process called photosyntheses.
Click here for more detailed information on
SCIENCE PHOTOS
SPO VIDEO: How to Make a Wet Mount of Onion Bulb Epidermal Cells
Margin
of
Elodea leaf @ 100xTM.
 | ||||||