| ||||
Mode of Action of
Sulfonamide Antibiotics
There are many different classes of antibiotics
each exerting a different type of inhibitory effect that specifically impacts bacteria. Bacterial cells are
prokaryotic; primitive cells that differ significantly from humans’
Article Summary: Antibiotics are chemotherapeutic agents used to inhibit or kill bacteria. But how do sulfa drugs destroy these microbes without hurting our cells?
MOA of Sulfronamide (Sulfa Drug) Antibiotics
You have free access to a large collection of materials used in a college-level introductory microbiology course. The Virtual Microbiology Classroom provides a wide range of free educational resources including PowerPoint Lectures, Study Guides, Review Questions and Practice Test Questions.
SPO VIRTUAL CLASSROOMS
Sulfa drugs exert their bactericidal effect by inhibiting a metabolic pathway that is necessary for DNA synthesis (replication).
Each article in this series covers a specific class of antibiotic and includes the following information:
- a list of the specific antibiotics that fall in the class (generic and brand names)
- mode of action
- type of infection the antibiotic class to against
- type of bacteria inhibited or killed
- pros and cons of using the class of antibiotics
Sulfonamide Antibiotics (Sulfa Drugs)
Sulfa drugs are synthetic antimicrobial agents that contain the sulfonamide group. German bacteriologist and pathologist Gerhard Domagk was awarded the 1939 Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine for discovering the antibacterial effects of prontosil red, a dye which contained the active component, sulfanilamide.
Some representative sulfonamides include:
- sulfacetamide
- sulfadimethoxine
- sulfadoxine
- sulfamethoxazole
- sulfasalazine
- sultiame
- sumatriptan
Sulpha is an alternate spelling of the common name for sulfa drugs or sulfonamide antibiotics.
Sulfanomides Mode of Action
Antibacterial sulfonamides target a bacterial metabolic pathway as competitive inhibitors of the enzyme dihydropteroate synthetase, DHPS. Dihydropteroate synthetase activity is vital in the synthesis of folate, and folate is required for cells to make nucleic acids, such as DNA or RNA. So if DNA molecules cannot be built, the cell cannot divide, and the effect is bacteriostatic (rather than bactericidal).
Sulfa drugs do not cause the same disruption in animal cells, because our cells do not synthesize folate. Since we can’t make folate, we need to consume it, and folate is a dietary requirement.
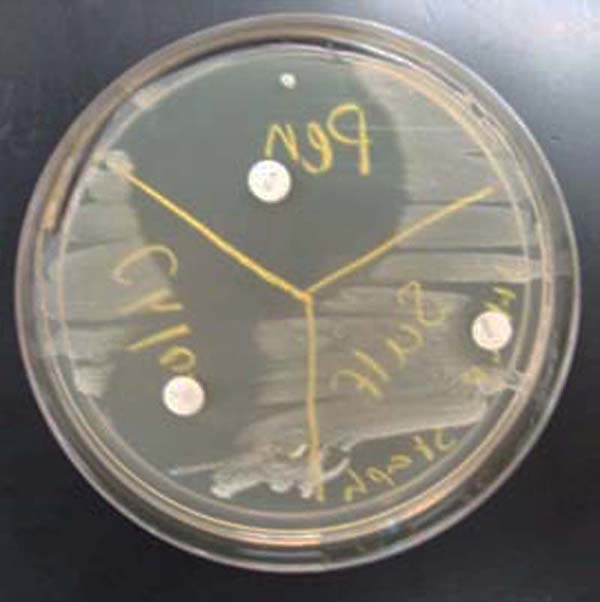
TSY agar inoculated with Staphylococcus. Three antibiotic sensitivity disks appear on this medium: penicillin, sulfa, and ciprofloxacin (clockwise from top). Note the "zone of inhibition" around each antibiotic disk. The larger the zone of inhibition, the more effective the antibiotic is against the bacteria.
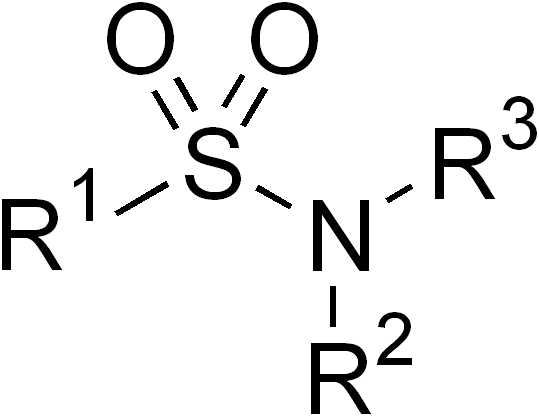
General chemical structure of a sulfonamide.
Page last updated: 8/2015
 | ||||||
HOME MICROBIOLOGY EXPERIMENT FROM SPO
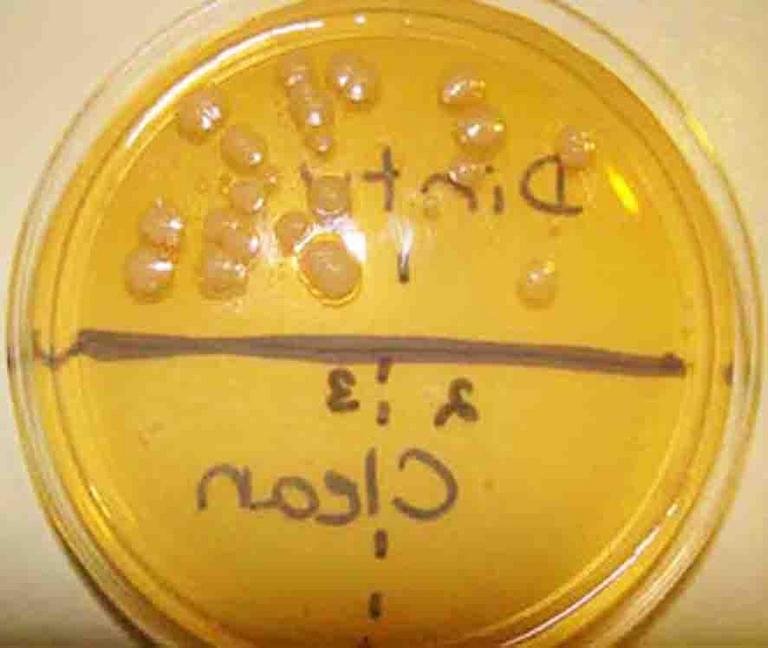
TSY agar with sample from dirty dishes on top (note bacterial colonies that grew), and sample from cleaned dishes on bottom.
Main Classes of Antibiotics
- Cephalosporins (a Beta-lactams)
- Penicillins (a Beta-lactam)
- Quinolones (Fluoroquinolones)
- Sulfonamides (Sulfa Drugs)