| ||||
The Basics of the Electron Transport Chain - P3
More Helpful Resources on Metabolism & Electron Transport
- Electron Transport Chain animation from Molecular & Cellular Biology Learning Cntr.
- Electron Transport Chain click through animation by Graham Kent Bio231 Cell Bio.
- Electron Transport System & Formation of ATP (Quiz 1) by McGraw-Hill.
- Electron Transport System & ATP Synthesis (Quiz 2) by McGraw-Hill.
3. Phosphorylation of ADP (The payoff!)
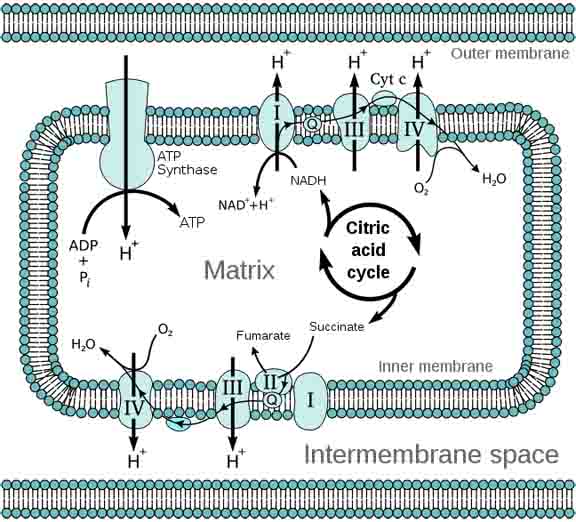
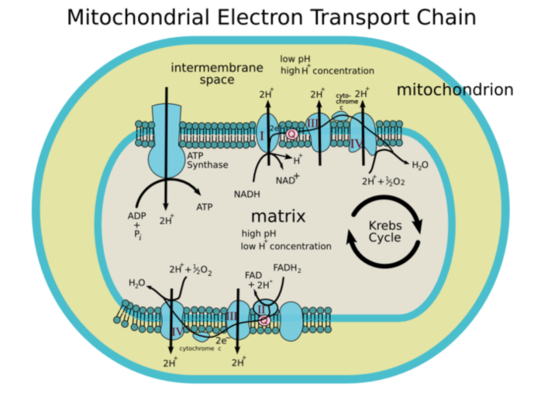
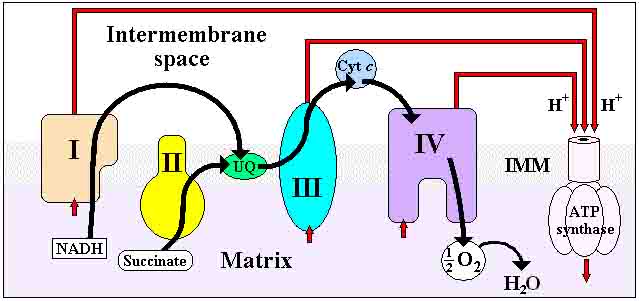
The hydrogen ions (H+), on the side of the membrane where most concentrated, will eventually flow back across the membrane, down the proton gradient, through an enzyme called ATP synthase.
As each H+ moves back across the membrane, the enzyme ATP synthase phosphorylates (adds a phosphate to) adenosine diphosphate (ADP) to make the high energy molecule ATP, which can be used for many different energy-requiring reactions throughout the cell.
Page last updated
3/2016
SPO VIRTUAL CLASSROOMS
Animated Video on the Electron Transport Chain
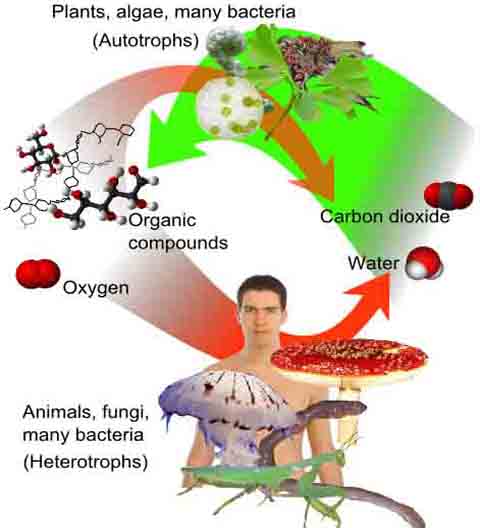
Electron Transport Chain in Mitochondria: Black arrows represent electron transport. Red arrows represent hydrogen ions (H+).
PAGE 3 < Back to Page 2
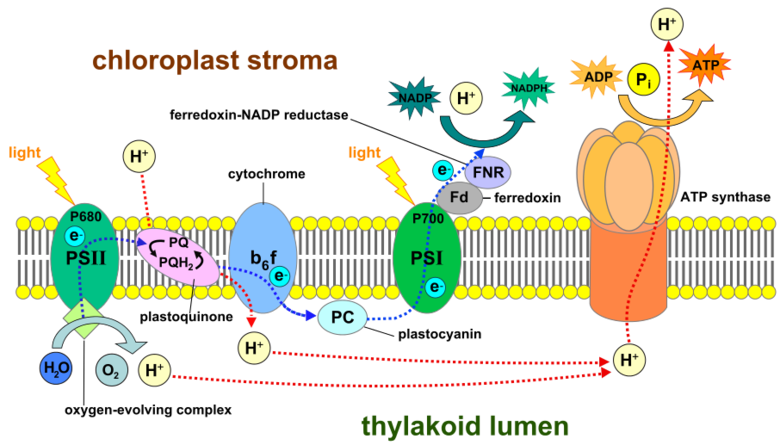
Electron Transport Chain in Thylakiod Membrane of Chloroplast
You have free access to a large collection of materials used in a college-level introductory Cell Biology Course. The Virtual Cell Biology Classroom provides a wide range of free educational resources including Power Point Lectures, Study Guides, Review Questions and Practice Test Questions.
 | ||||
See the
for a fun, hands-on way to teach students the steps of the ETC!
Want To Learn More About Metabolism and the Electron Transport Chain?