| ||||
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) Energy Nucleotide - P2
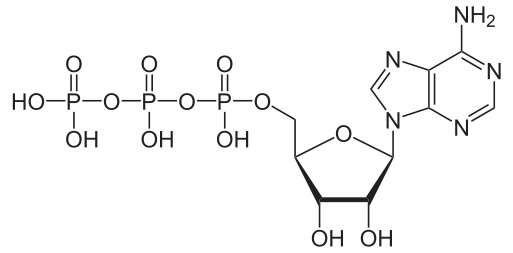
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
SPO VIRTUAL CLASSROOMS
The SPO website is best viewed in Google Chrome,
Microsoft Explorer
or Apple Safari.
 | ||||||
Need Help with Chemistry?
SPO offers free PowerPoint lectures, sample test
questions, review questions and assignments on many different science topics.
Below are links to those that relate to chemistry:
You have free access to a large collection of materials used in a college-level introductory Cell Biology Course. The Virtual Cell Biology Classroom provides a wide range of free educational resources including Power Point Lectures, Study Guides, Review Questions and Practice Test Questions.
Page last updated: 9/2015
How Is ATP Made?
ATP is produced by autotrophs during photosynthesis, as described above, and is also produced by both autotrophs and heterotrophs during a process known as cellular respiration.
In cellular respiration food molecules are catabolized (broken down) and the released energy is transformed into ATP.
most commonly glucose, are the food source typically used to make ATP. Carbs can be catabolized through the processes of cellular respiration
or fermentation.
PAGE 2 < Back to Page 1
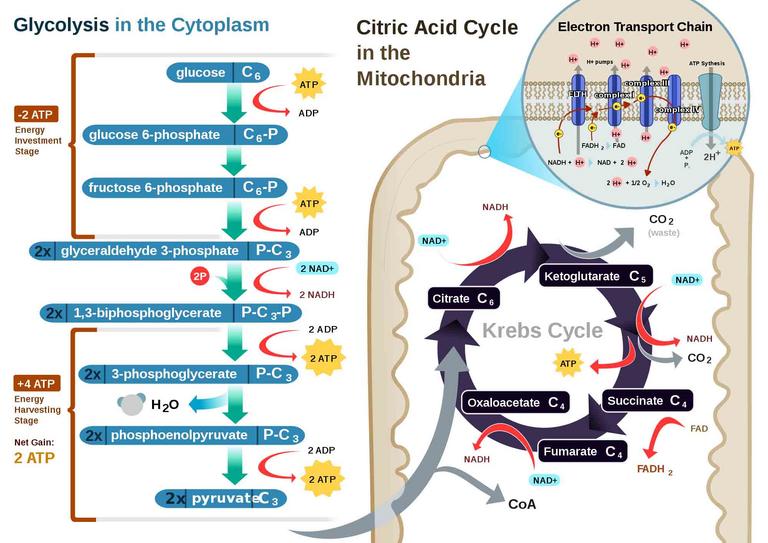
Aerobic cellular respiration utilizes glycolysis, synthesis of acetyl-CoA, Krebs cycle, and electron transport chain; the end result being the complete breakdown of glucose into carbon dioxide, water and ATP energy. Through these catabolic pathways, up to 38 molecules of ATP can be made from every molecule of glucose. Oxygen is a vital component of this highly efficient process, hence the name "aerobic respiration".
Anaerobic respiration and fermentation are used to derive energy from glucose by organisms that either cannot survive in the presence of oxygen or don’t always have access to oxygen. Fermentation is less energy efficient than aerobic or anaerobic cellular respiration. Still, even in the absence of oxygen, anaerobes can utilize glycolysis to break down glucose and ultimately net a only two ATP.
Where is ATP Made?
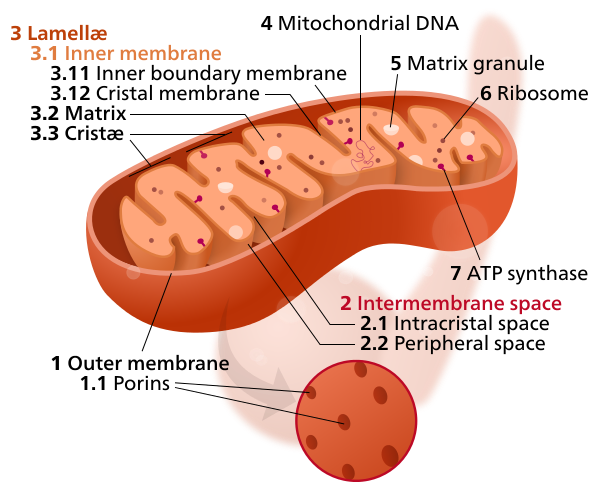
In eukaryotic cells, complex cells that possess a nucleus, ATP is synthesized in tiny energy factories called mitochondria. In more primitive
prokaryotes ATP synthesis occurs in the cytoplasm and cytoplasmic membrane.
Sources
- Bauman, R. (2014) Microbiology with Diseases by Body System, 4th ed., Pearson Benjamin Cummings.
- Park Talaro, K. (2008) Foundations in Microbiology, McGraw-Hill.
- ATP and Energy Storage interactive animation from Dr. Saul's Biology In Motion.
- What ATP Is and How It Works video by Leslie Samuel TV.
- ATP: Adenosine Triphosphate lecture from Kahnacademy.
- Organic Chemistry Lecture Main Page from the Virtual Cell Biology Classroom.
- Aerobic Respiration Lecture Main Page from the Virtual Cell Biology Classroom.