| ||||
Animal Cell Structures, Functions & Diagrams - P3
Other Animal Cell Components and Organelles
- Cytoplasm: The inside of the cell, between the nucleus and plasma membrane, is filled with a gel-like fluid in which the organelles are suspended. The liquid portion of cytoplasm is called cytosol.
SPO VIRTUAL CLASSROOMS
You have free access to a large collection of materials used in a college-level introductory Cell Biology Course. The Virtual Cell Biology Classroom provides a wide range of free educational resources including Power Point Lectures, Study Guides, Review Questions and Practice Test Questions.
NEW! FREE Educational Materials on Cell Structure
Sources and Helpful Eukaryotic Cell Links
- Becker, W. M. et. al. (2009) The World of the Cell. Pearson Benjamin Cummings.
- Eukaryotic Cell Interactive Animation from Cells Alive.
- Inside a Cell, interactive cell diagram from University of Utah.
- Eukaryotic Cell Tour interactive exercise.
- Endoplasmic Reticulum & Golgi Apparatus interactive lesson
- Cell Structure Interactive Animation from Wiley.com.
PAGE 3 < Back to Page 2
SPO VIDEO: How to Make a Wet Mount of Stained Epithelial Cheek Cells
End of article ...
Page last updated: 1/2016
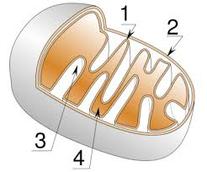
MITOCHONDRION
1. Inner membrane
2. Outer membrane
3. Cristae
4. Matrix fluid
- Cytoskeleton: This network of fibers and tubules is present throughout the interior of the cell, providing support, anchoring organelles, helping with intracellular transport and cell division.
- Centrioles and centrosomes: Only present in animal cells and some fungal cells, a pair of centrioles is located near the nucleus, in a region called the centrosome. These organelles are composed of microtubules, help build flagella and cilia, and form mitotic spindles during cell division.
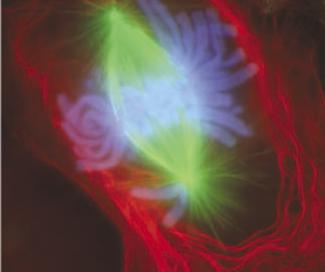
Animal cell undergoing mitosis and stained with with fluorescent dyes.
The material stained green are the mitotic spindles, the material stained red is the cell membrane and some components of the cytoplasm near it, and the material stained light blue are the chromosomes..