| ||||
MOA of Cephalosporin Antibiotics - P2
You have free access to a large collection of materials used in a college-level introductory microbiology course. The Virtual Microbiology Classroom provides a wide range of free educational resources including PowerPoint Lectures, Study Guides, Review Questions and Practice Test Questions.
SPO VIRTUAL CLASSROOMS
Sources & Resources
- Bauman, R. (2014) Microbiology with Diseases by Taxonomy. Pearson Benjamin Cummings.
- Park Talaro, K (2008) Foundations in Microbiology, McGraw Hill.
- Bayarski, Yuri, "Antibiotics and Their Types, Uses and Side Effects."
- Microbiology In the Home: Tips To Sanitize Your House and Keep Your Family Healthy, Household Microbiology article from Science Prof Online.
- Microbial Control Laboratory Exercise Main Page from the Virtual Microbiology Classroom.
* The information in this article is not meant to be used for self-diagnosis or treatment of illness. If you are sick, seek help from a trained medical professional, not a computer.
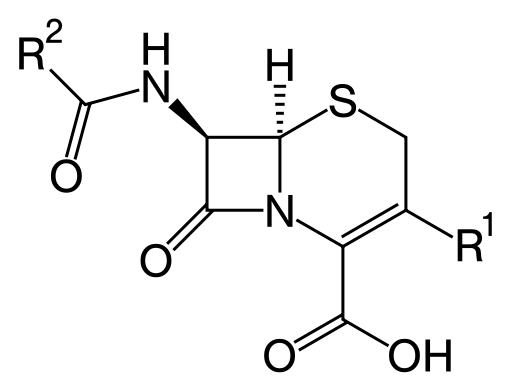
Cephalosporin core structure, where "R" is the variable group.
Page last updated: 8/2015
Type of Infections Cephalosporins Are Used Against
Cephalosporins are used to treat a wide range of infections, including pneumonia, strep throat, various staph infections including those of the skin, tonsillitis, bronchitis and gonorrhea. Cephalosporin is also commonly used prophylactically with surgical procedures, as a preventative measure to avoid infection.
Antimicrobial Spectrum of Cephalosporins
First-generation cephalosporins are mainly effective against Gram-positive bacteria.
The SPO website is best viewed in Google Chrome, Microsoft
Explorer or Apple Safari.
PAGE 2 < Back to Page 1
The generations to follow have successively increased activity against Gram-negative bacteria, with the trade-off of then being less effective against Gram-positive microbes.
Side Effects of Cephalosporins
Cephalosporins are similar to penicillin in action and side effects, and are often used in patients with and allergy to penicillin. The most common side effects of cephalosporin are mild diarrhea, headache, sore mouth or tongue, vaginal itching and discharge, white patches in the mouth and/or tongue. These vaginal and oral side effects are due to an increase in yeast population when competing bacteria are removed.