| ||||
Evolution: Just a Theory? - P2
SPO VIRTUAL CLASSROOMS
How Does Evolution Work?
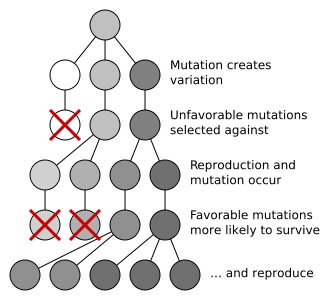
Evolution can be defined as inheritable change in a population that ultimately results from the interaction of individuals with their environment. And its action over very large stretches of time explains the origin of new species, occasionally the elimination of existing species and ultimately the vast diversity of the biological world.
Today’s species are related to each other through common decent (ancestors that they share) and are products of evolution over billions of years.
Page last updated: 11/2015
You have FREE access to a large collection of materials used in a college-level introductory biology course. The Virtual Biology Classroom provides a wide range of free educational resources including PowerPoint Lectures, Study Guides, Review Questions & Practice Test Questions.
PAGE 2 < Back to Page 1
Key concepts of evolution:
- Any change must be inheritable (able to be passed on to the next generation).
- These changes are regulated by natural selection.
Natural Selection
Natural selection a theory on the mechanism of evolution, the process in nature by which only the organisms that are best adapted to their environment tend to survive and transmit their genetic characteristics to the next generation (reproduce) in higher numbers. Individuals less well adapted to their environment tend to be eliminated.
 | ||||||
SPO is a FREE science education website. Donations are key in helping us provide this resource with fewer ads.
Please help!
(This donation link uses PayPal on a secure connection.)
Sources & Resources
- Brown, Bryson (2007) Evolution: A Historical Perspective. Greenwood Press.
- Campbell & Reece (2005) Biology, 7th Edition. Pearson.
- Understanding Evolution website from University of California Museum of Paleontology.
- Evolution website from PBS.
- Fun Interactive Evolution Activity from the BBC's GCSE Bitesize.
- New NOVA Evolution website from PBS.
- Interactive Evolution Timeline from John Kyrk.
- Pre-Darwinian Evolutionary Theory, "Class Notes" from SPO.
- Charles Darwin and Evolutionary Theory, "Class Notes" from ScienceProfOnline.
- Evolution: Natural & Artificial Selection, "Class Notes"
- Role of Genetic Mutation in Evolution, "Class Notes" from SPO.
- "Darwinvaganza" Radiolab episode from WNYC.
- Charles Darwin Biography episode.
- Voyage of the Beagle, by Charles Darwin. Audio reading from LibriVox.
- "In Defense of Darwin" Radiolab episode featuring Richard Dawkins.