| ||||
Peptide Bonds & Protein Structure - P2
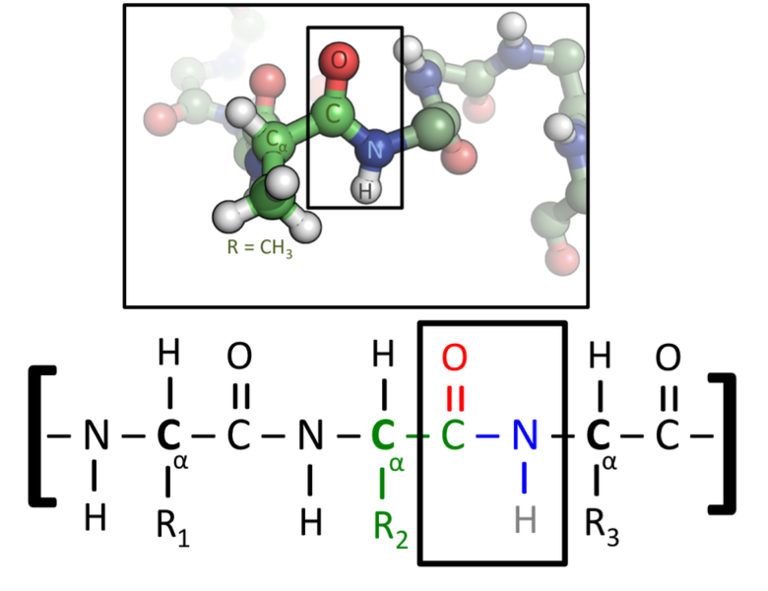
A peptide bond (circled) between Leu and Thr in a protein structure. Green=carbon, red=oxygen, blue=nitrogen.
Protein Structure and Function
Structure of a protein is directly related to its function, so that anything that severely disrupts the shape will also disrupt the function. Denaturation is alteration of a protein shape through some form of external stress (for example, by applying heat, acid or alkali), in such a way that it can’t carry out its cellular function.
Levels of Protein Structure
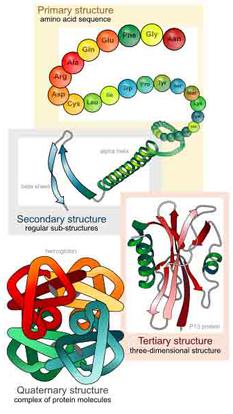
Every protein has at least three levels of structure: primary, secondary and tertiary. Quaternary structure is a grouping of more than one amino acid chain.
SPO VIRTUAL CLASSROOMS
Peptide Bonds
Peptide bonds are the covalent bonds which link amino acids together into chains, like the beads on a necklace. A dipeptide is composed of 2 amino acids linked together, a polypeptide is more than two.
Page last updated: 9/2013
The SPO website is best viewed in Google Chrome,
Microsoft Explorer or Apple Safari.
The Virtual Cell Biology Classroom provides a wide range of free educational resources including Power Point Lectures, Study Guides, Review Questions and Practice Test Questions.
Page last updated: 8/2015
FREE Printable
study aid.
See the
Organic Chemistry Lecture PPT for info that will help you complete this table.
PAGE 2 < Back to Page 1
- Primary Structure: Amino acids linked together by peptide bonds into a peptide chains.
- Secondary Structure: Ionic bonds, hydrogen bonds, and hydrophilic / hydrophobic characteristics cause many polypeptide chains to fold into coils (α–helices), or accordion-like structures (β-pleated sheets). Proteins are typically composed of both α–helices and β-pleated sheets linked by short sequences of amino acids.
- Tertiary Structure: This is the three-dimensional structure of single protein molecule; a spatial arrangement of secondary structures.
- Quaternary Structure: This level of structure represents a complex of several protein molecules or polypeptide chains, which function as part of the protein complex.
Sources and Helpful Organic Chemistry Links
- Bauman, R. (2014) Microbiology
- Park Talaro, K. (2008) Foundations in Microbiology, McGraw-Hill.
- Biomolecules: The Proteins interactive animated lesson from Wisc-Online.com.
- Protein Denaturation animation and quiz from McGraw-Hill.
- Heat Changes Protein Structure: Frying an Egg animation and quiz from Norton.
- Organic Chemistry Lecture Main Page from the Virtual Cell Biology Classroom.