| ||||
Binomial Nomenclature:
What's In a (Scientific) Name?
Article Summary: Here's a clear summary of the Linnean system of binomial nomenclature, the scientific way to name living things with a two part generic (genus) and specific (species) name.
Biological Classification & Binomial Nomenclature
Carl Linnaeus
(1707-1778), Swedish physician and botanist, was the founder of modern taxonomy. He used his super-smart Homo sapiens brain to come up with a system called binomial nomenclature used for naming living things and grouping similar organisms into categories.
SPO VIRTUAL CLASSROOMS
 | ||||||
Page last updated: 3/2016
Taxonomy is used in the related discipline of biological systematics, when scientists try to determine the evolutionary relationships between organisms (how closely related they are to each other).
Today, biologists still use the Linnaean system of classification, but advances in the fields of genetics and
evolutionary theory have resulted in some of Linnaeus’ original categories being changed to better reflect the relationships among organisms.
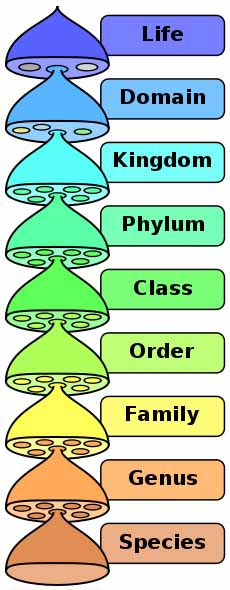
Use this sentence to remember the levels of biological classification in order from most general to most specific: "Little darling King Phillip came over for green soup."
See the Biological Classification Lecture Main Page for all of our FREE teaching materials on this topic!
Hierarchy of Biological Classification
All life can be classified in increasingly specific groups, starting by sorting all life into three Domains (Archaea, Eubacteria and Eukaryota) and ending with the most specific category, the individual species. And every species has its own name.
Binomial Nomenclature
Also called binary nomenclature, this formal system of naming organisms consists of two Latinized names, the genus and the species. All living things, and even some viruses, have a scientific name.